
Optimising 3D RT EarthCARE product using geostationary observations and AI


Optimising 3D RT EarthCARE product using geostationary observations and AI

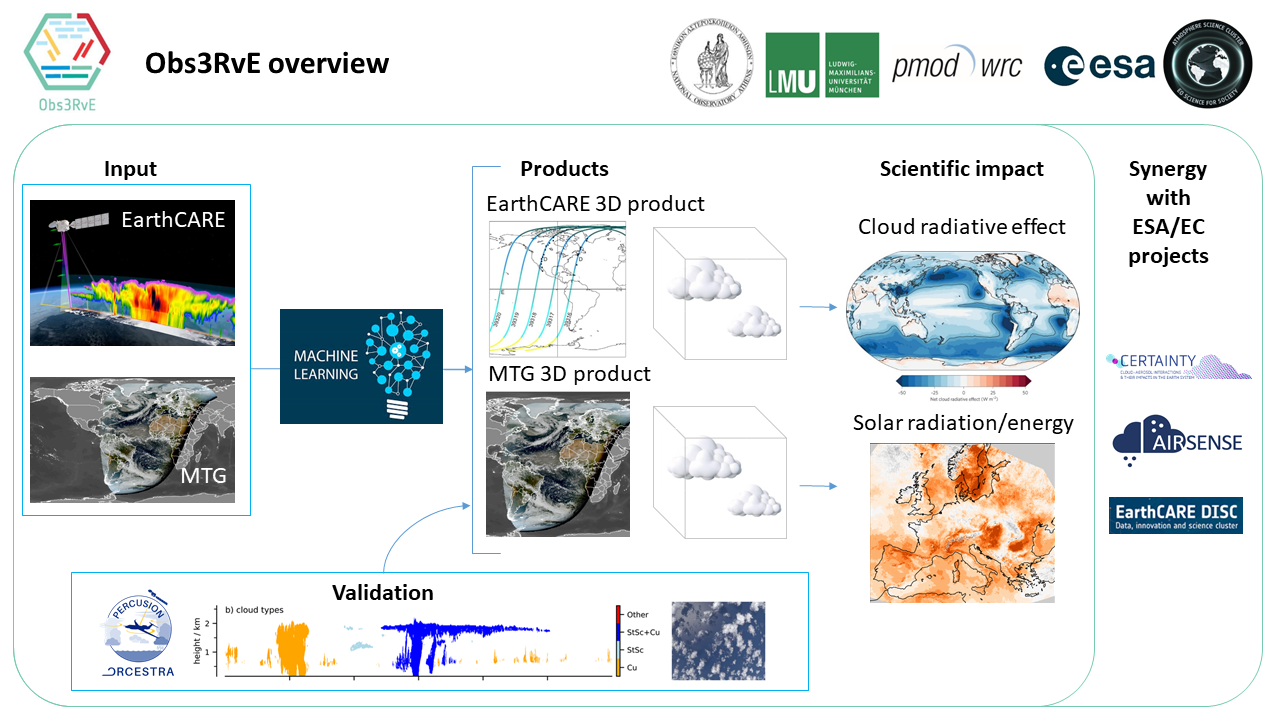
Obs3RvE (Optimising 3D RT EarthCARE product using geostationary observations and AI) is a project funded by ESA, in the framework of EC-ESA Earth System Science Initiative, that aims to produce ground-breaking scientific results through the exploitation of the EarthCARE mission.
Obs3RvE proposes an innovative approach towards more accurate quantification of the 3D radiative effects of clouds and their impact on climate, utilising the observations of EarthCARE and MTG missions with AI tools. The results of Obs3RvE will also aim to extend the contribution of the EarthCARE data on solar energy applications, a scientific domain beyond the mission primary objectives.

National Observatory of Athens (NOA)
NOA is a pioneering research institution with over 170 years of international presence in science and education. NOA excels in observing the atmospheric environment, focusing on physical processes, interactions, and extreme events. NOA participates in the project with researchers from the Institute of Astronomy, Astrophysics, Space Applications & Remote Sensing (IAASARS) under the Remote sensing of Aerosols, Clouds and Trace gases (ReACT) Unit and the BEYOND EO Centre.

ReACT/NOA
The experimental and theoretical work of the ReACT/ΝΟΑ group, is dedicated to the application of measuring methodologies for the remote sensing of aerosol and clouds, along with their interactions, processes and their radiative impacts. ReACT/NOA activities are targeted towards understanding physical and chemical processes in the atmosphere, seizing the opportunity provided by the complex and vulnerable Mediterranean environment, utilising advanced ground-based and space-borne remote sensing observations and theoretical models.

BEYOND/NOA
The BEYOND Center of Excellence for Earth Observation Research & Satellite Remote Sensing was established through competitive European Union funding. BEYOND focuses on developing innovative, integrated solutions using big Earth Observation data and cutting-edge AI to address societal and environmental challenges. The centre’s efforts are directed toward enhancing resilience and response capabilities in natural disaster management, assessing and mitigating climatic risks, supporting sustainable agricultural practices, advancing public health applications, and optimising renewable energy solutions.

Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU)
The Meteorological Institute of the Faculty of Physics at the Ludwig-Maximilians-University (LMU) in Munich includes the Chair of Experimental Meteorology (Prof. Bernhard Mayer) and the Chair of Theoretical Meteorology (Prof. George Craig). The latter performs research in atmospheric dynamics, predictability, and data assimilation. The experimental meteorology section performs radiative transfer modelling, cloud and aerosol physics, and active and passive remote sensing of clouds, aerosols and trace gases.
The strength of the Chair of Experimental Meteorology is the combination of experimental, technological, and theoretical experience over many years, which allows innovative process development and scientific assessment of new measurement technologies. The group has been developing the publicly available libRadtran RT package which is one of the most common RT models and has been used for more than 1000 publications, in numerous projects including a number of ESA studies. The Monte Carlo Code for the phYSically correct Tracing of photons in Cloudy atmospheres (MYSTIC), also developed by the group, is one of the most advanced 3D RT solvers, which allows handling 3D clouds as well as inhomogeneous surface albedo and structured terrain.

Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos / World Radiation Center (PMOD/WRC)
Radiation measurements are a fundamental part of meteorological observation and climate monitoring. Research has been conducted on solar irradiance at the PMOD since 1907. In 1971, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) gave the PMOD the additional mandate of serving as the World Radiation Center (WRC). The WRC plays a crucial role in maintaining quality standards in global climate monitoring programmes. The WRC fields of activity are divided into four Sections in which the measurement of solar radiation is the central focus of each one. While the PMOD/WRC develops new techniques and instruments to measure solar radiation, measured data is analysed and used for instance to investigate Climate Change. PMOD/WRC is the World meteorological Organization global solar radiation and aerosol optical depth center providing the global solar irradiance “scale”.
20/06/2025
The Kickoff Meeting of Obs3RvE project took place on June, 20th, 2025. The meeting was held in an online format, with a total of 17 participants. This successful kick-off meeting is a strong start of our challenging project!
05/01/2026
Obs3RvE team has participated in the EarthCARE Science and Validation Workshop 2025, held at the University of Tokyo from 1 to 5 December 2025. The workshop, co-organized by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the European Space Agency (ESA), brought together experts from around the world to present and discuss topics related to the EarthCARE mission, its scientific results to date, and findings from the validation of the mission’s products.
Obs3RvE activities were presented in the following talks and posters:
Obs3RvE publications in peer-reviewed journals and conferences will be available soon.
The Obs3RvE data will be available soon.